CONTENTS:
- What is Brushless motor? How does it work?
- Brushless motor design and main parts
- What is a brushed motor? How does it work?
- Pros and Cons of Brushed DC motor
- Main applications. What is better?
Difference between brushed and brushless motors in a nutshell
Electric Motors are devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical ones. The efficiency of that process depends on its design and type of current (AC or DC).
So, what is the difference between brushed and brushless motors in a nutshell?
- Brushless motors have absence of brushes in assembly, and they are more compact. Instead, they need to be equipped with additional commutating devices (controllers, rotary encoders, drives).
- Brushed motors are cheaper and simpler. They can be wired directly to DC source and have simple elementary control (like a switch).
- In brushless variations, their rotor rotates electronically on the other hand; brushed armature rotates mechanically (current transmitted through brushes).
- Brushless ones have three wires for connection and the brushed have two.
- Brushless motors have a bigger efficiency (85-90%) then brushed (75%-80%). This means that with the same power the first ones convert a large rotational force, because they do not create friction and do not lose much heat during their operation.
Thus, we can draw our first brief conclusion. Brushless motors have higher performance, efficiency, and increased stability. On the other hand, Brushed electric motors have lower prices and are easier to maintain.
For a bigger difference let`s look at them in detail.
What is Brushless motor? How does it work?
The operation principle of both motor types is generally similar. It is based on the interaction of a permanent magnet in the rotor and an electric magnet in the stator.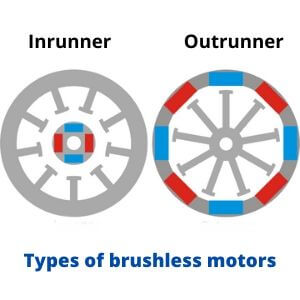
Brushless DC motor (it is also called BLDC or just BL) is a synchronous device and acts like PMSM (Permanent magnet synchronous motor). Therefore, its working principle is based on self-synchronized frequency regulation when their rotor and stator contacting with the same frequency.
BLDC motors come in two types:
- Out-runner
- In-runner
In the first case, the rotor is located above the stator, and in the second, under it. Let’s take a look at how it works on out-runner version as an example.
In such design, the rotor has permanent magnets and stator has a coil arrangement that forms an electrical magnet. The basic principle of operation is based exactly on their interaction.
A power from source makes coils energized, and they create a magnetic field according to Faraday law. When it happens, these energized coils are attracted to opposite poles located on rotor. These coils are installed in the rotor, so it starts to rotate with them.
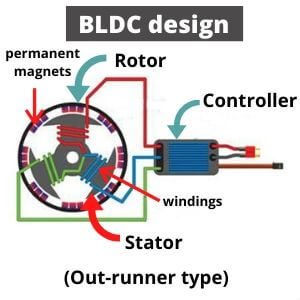 When they approach to opposite pole, power turns off and commutator starts to energize a next pair. The next pair of coils are also attracted, thereby moving the rotor further. Then such action is repeated continuously.
When they approach to opposite pole, power turns off and commutator starts to energize a next pair. The next pair of coils are also attracted, thereby moving the rotor further. Then such action is repeated continuously.
BLDC have a special design that allows user to supply power to any coil, so it can quickly change torque and rotation speed. Brushless motors have a compact size with high speed and precise positioning at the same time.
BL motors generate no friction; hence they produce more rotation force instead of heat. This is achieved due to the lack of brushes. Instead of them, integrated commutating devices monitor and regulate a rotor position, speed of rotation, and steady distribution of current across the coils.
Brushless motor design and main parts
A common motor of that type has a three-phase winding on the stator and a permanent magnet on the rotor. It is also made in single, dual, or three-phase variations. As was mentioned above, the stator winding creates a rotating magnetic field, which drives the magnetic rotor into motion. To form such magnetic field, a three-phase voltage is applied to the winding.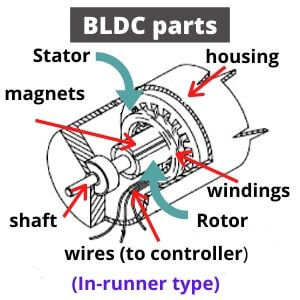
So how does the system know which coil is energized and which should be energized? For this purpose, a special electronic controller is used. Such integrated commutating device turn on current to orthogonal (perpendicular) windings. It also contains sensors that determine a rotor position. The most often hall sensors are used but sometimes photoelectrical, inductive sensors, and resolvers perform such tasks.
To change the direction of rotation, the controller changes connection of two phases. It also can work as stepper or servo motor.
Advantages and disadvantages of brushless DC motor
The main advantages of a brushless motor
- long service life;
- low noise level;
- high-efficiency indicators – about 90%;
- maximum rotation speed is achieved quickly;
- do not spark form during operation;
- additional cooling resources are not required;
- there are no mechanisms that need regular maintenance.
The main disadvantages of brushless motors
- complex management system;
- limited resource of electrical components;

- high price due to expensive components.
- need additional commutating devices to work (commutators, encoders, drives)
What is a brushed motor? How does it work?
Brushed motors are the most common DC motor. As noted above, its principle also consists in the attraction of two magnets with opposite poles.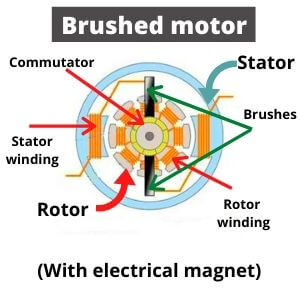
The main parts of such motor are:
- Stator
- Rotor (armature)
- Brushes
- Commutator
Permanent or electrical magnets are placed on the stator and form a constant magnetic field. DC motors with electrical magnets are powered with the same dc source that armature.
Such motors can be of two main types:
- Shunt motors (with parallel connection)
- Serial motors (with serial connection)
Serial motors have a good start torque but its speed drops didactically with load. Opposite them, the parallel motors have worse start torque, but they can perform a constant speed irrespectively to acting load.
The rotor is connected to dc power source by brushes. Brushes are attached into commutator. Different windings are connected with different segments of such commutators. When they are energized, they create a magnetic field. When the rotor rotates, their magnetic fields change. This field switching is called commutation.
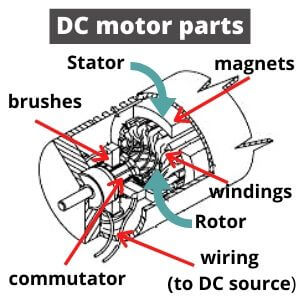 The current flows from the source to the windings, which as a result of the Lorentz law create a magnetic field and begin to interact with the magnets on the stator. The brushes (that made of generally of graphite) transfer power to the armature. To maintain their constant fit to the commutator, the springs exert pressure on them.
The current flows from the source to the windings, which as a result of the Lorentz law create a magnetic field and begin to interact with the magnets on the stator. The brushes (that made of generally of graphite) transfer power to the armature. To maintain their constant fit to the commutator, the springs exert pressure on them.
In the simplest mechanism with one loop of armature, an issue may happen when the armature becomes perpendicular to magnetic flux. In this case, its torque is equal to zero and the movement is interrupted for a short period. Therefore, for a smoother movement, additional loops are added to the design. The more of these loops, the smoother movement will be.
During the operation of such engines, Internal Electromotive (EMF) and Counter Electromotive (Back EMF) Forces often arise in accordance with the laws of Faraday and Lorenz. Because of this, a large amount of heat is generated. Therefore, in large and powerful motors, it is extremely needed to install additional cooling devices to avoid fire.
Pros and Cons of Brushed DC motor
The main advantages of brushed motors:
- low cost;
- simple design and wiring;
- easy maintenance;
- reliable to mechanical and vibration shocks.
The main disadvantages of brushed motors:
- brushes wear out quickly;
- have an electromagnetic noise;
- sparks form during operation;

- the mechanism overheats and smokes;
- low efficiency (about 60-80%);
- due to the high friction of the brushes, the service life is reduced.
Main applications. What is better?
Brushless motors, firstly, offer high performance and long life cycle. Such models are needed in areas where high rotation speed and resistance to overheating are required at the same time. Such equipment is used as part of the cooling system, in robotics, medical equipment, CNC machines, and other expensive and crucial industrial equipment. Brushless devices are more powerful than brushed ones with the same size. It is also used in areas when electric motors with a high lifespan and lack of maintenance are required.
The common brush dc motor has less power and stability. However, it is cheap and simple. Therefore, those devices perform not complicated and long-term tasks. Such equipment is used in the domestic sphere: in automobiles, hoisting mechanisms, in children’s radio-controlled models, and some household tools (like a drill). They need regular maintenance due to brush friction and quick wear, but they are quite reliable to resistance in industrial harsh environments.
On our website Eltra-Trade.com you can find the most popular models of Siemens and ABB motors.
